Fundamental Understanding: What Do Laser Printers Use?
Introduction
Laser printers revolutionize the way we print documents, enhancing print speed and print quality. But what exactly do these machine marvels utilize to achieve such functioning? This article discusses in detail the fundamental components and resources laser printers employ, contributing to their high-resolution crisp output, power efficiency, and sustainability.
Grasping the Basic Concept of Laser Printing
A simplistic perspective of laser printing can be quite straightforward, but delving deeper exposes an intricate process that merges technology and innovation. The following points give a detailed account of the core principles governing laser printing:
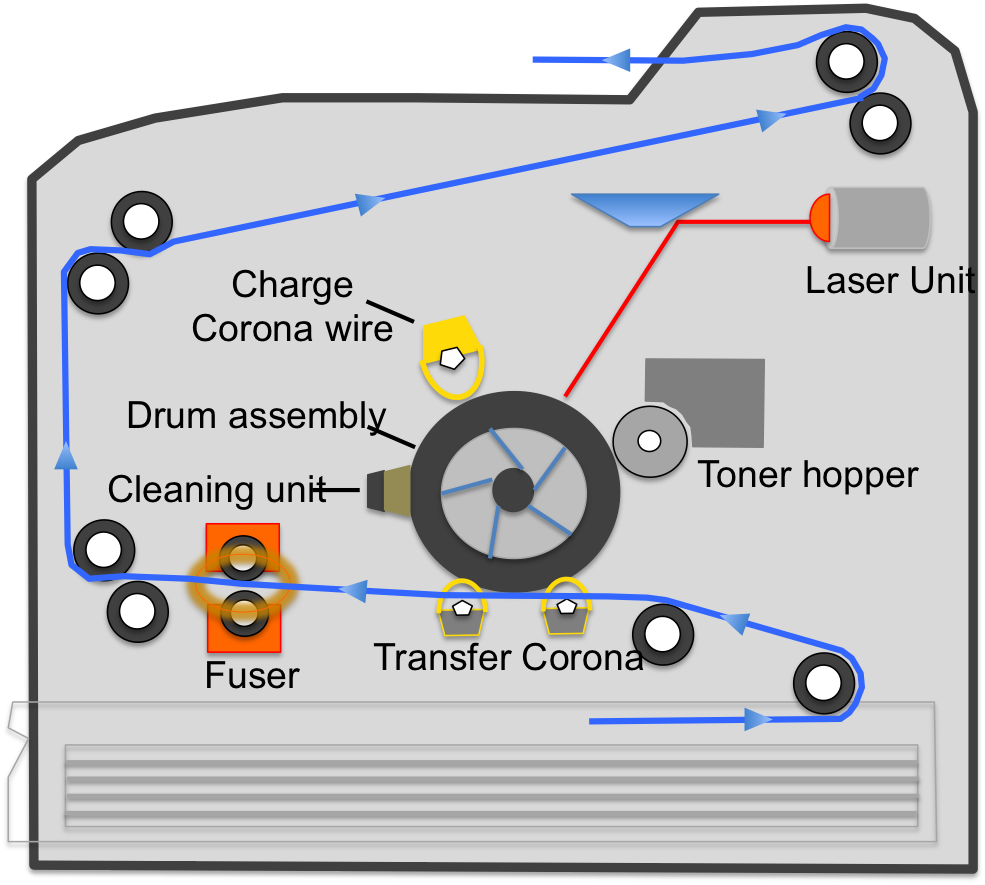
- Underpinning Mechanism: Central to all laser printers is the xerographic printing process- a digital printing technique that quickly yields high-quality text and images on plain paper.
- The Light Source: Unlike traditional photocopiers using photocopier technology, laser printers employ a laser beam as their primary light source. This laser beam plays an essential role in projecting the printed page's image.
- The Photosensitive Drum: A crucial component in the printing process, the photosensitive drum, interacts with the laser beam. The electrically charged drum is selectively exposed to the laser, creating a temporary image of the targeted page.

This simplification of laser printing demonstrates the amalgamation of various parts and technologies to provide sharp, rapid printouts for users.
Diving into the Core: What’s Inside a Laser Printer?
Exploring the insides of a laser printer reveal few key components that contribute to its extraordinary performance. This intricate architecture is characterized by:
1. Drum Unit/Photosensitive Drum: Playing an integral part in the printing process, the photosensitive drum captures the laser beam's image of the page. This drum rotates at high speed during the process.
2. Toner Cartridge: The toner cartridge is unique to laser printers and replaces the traditional liquid ink. It holds the toner - a fine powder that forms the sharp, high-resolution images and text on paper.
3. Laser Unit: As the name suggests, laser printers utilize a laser unit. This laser beam reproduces an accurate image on the photosensitive drum, which then gets imprinted on the paper.
4. Rollers and Fusers: Finally, a set of rollers feed the paper into the machine. The heated fuser unit then melts the toner particles and binds them permanently onto the paper. This ensures that the text or image doesn't smudge or fade over time.
Understanding these integral parts helps to better appreciate the complex process behind a seemingly simple task of printing a sheet of paper.
Ink or Toner? Uncovering What Laser Printers Use
Unlike their inkjet counterparts, laser printers employ a unique form of "ink" - a powdery substance known as a toner. In essence, the differences between these materials are stark and greatly influence the final print quality and the printer's operations. Let’s unravel the specifics:
- Toner Composition: The toner, used by laser printers, is composed of pigment and plastic particles. This constituent composition of toner strands as one of the key elements distinguishing it from conventional liquid ink used in inkjet printers.
- Printing Process: The toner particles are fused onto the paper via the heating process, courtesy of the printer's fuser unit. This induces the creation of crisp, detailed text and graphics which are instantly dry upon printing, unlike inkjet prints that can smudge easily.
- Cost Comparison: While toners are generally pricier than liquid ink, their longevity tends to compensate for the initial higher purchasing cost. This becomes especially significant for users with extensive printing needs.
- Print Quality: Laser printers using toners ensure superior print resolution, producing sharper, high-definition images with richer colors and smooth gradients. This is of great worth in professional settings where high quality prints matter the most.
In conclusion, it's crucial to note that while the cost of toner may seem substantial at first glance, laser printer users often realize that their overall printing cost gets reduced in the long run. This is because of the superior longevity of the toner cartridges and the unfavorable 'cost-per-page' ratio of liquid ink cartridges, which inkjet printers use.
By comprehending the usage and benefits of toners, you can fully optimize your laser printer's operations, appreciate the print quality it affords, and realize its cost-effectiveness over time.
A Closer Look at the High-Quality Resolution of Laser Printers
Laser printers have carved a niche for themselves, due to their stellar capability to produce high-quality images and text. This high standard is owed to the accurate shapes and highly detailed images that a laser is able to render. Let’s unwrap some of the distinct features of these printers:
- Precision of the Laser: The laser's precision plays a key role in the creation of highly detailed and precise shapes. It enables the printer to provide superior print resolution, which is beneficial for all types of printing needs, from text to images.
- Quality of Toner Particles: The fineness of toner particles used in laser printers enables them to deliver smooth gradients and rich colors, contributing to a visually pleasing overall print.
- Excellent Resolution: Laser printers can produce resolutions from 600 x 600 dots per inch (DPI) to 2400 x 2400 DPI, meaning they are capable of rendering extremely detailed images. This is a significant benefit for users who print high resolution images or complex graphic designs.
- Improved Print Durability: The high-quality resolution output of laser printers also means that the resulting prints are more resistant to fading, discoloration, and smudging. This results in long-lasting prints that remain pristine over the passage of time.
By understanding the high-resolution capabilities of laser printers, users can better appreciate the gritty details and exceptional clarity their laser-printed documents possess. When it comes to achieving excellent printing standards, these modern marvels indeed hold a stellar repute.
How Do Laser Printers Utilize Power and Heat? An In-depth Analysis
Laser printers have evolved to intelligently manage energy and heat while operating. This discussion delves into understanding how they utilize power and heat.
Heat Utilization
The heat in laser printers is mainly generated by the fuser unit. Its role is fundamental yet power-consuming:
- The Fuser Unit: This part of the printer draws substantial power to heat the toner particles until they melt. Once in a liquid state, these granules are more manageable, bonding to the paper to produce a printed image.
Power Consumption
Laser printers utilize electricity strategically to maintain high output without alienating energy-conscious consumers:
- Initial Power Draw: To generate enough heat to melt the toner, laser printers draw a higher amount of electricity initially. However, this power demand drops significantly once the printer is no longer actively printing.
- Standby Mode: To conserve energy, the printer switches to a low-power standby mode when not in use. Not only does this mode lower power consumption, but it also reduces wear on the printer components.
- Deep Sleep Mode: Some advanced printer models even feature a 'deep sleep' mode that further reduces power consumption when the printer is idle for extended periods.
Recent statistics reveal that a laser printer uses approximately 300 to 700 watts of power during operation but reduces this use to about 30 to 50 watts during standby mode. Consequently, this adaptive use of power has contributed to laser printers earning Energy Star certifications, further promoting their use as an energy-efficient option in printing technology.
Conclusion
Understanding what materials and technology your laser printer utilizes allows you to use it more efficiently. Knowing that they use toner instead of liquid ink, appreciate the delicate, high-resolution prints, as well as their strategic use of power, can help you optimize their usage. Geeky details underlying laser printers reveal their high-end functionality, contributing to their popularity in professional and domestic settings.
Related FAQs about what do laser printers use
Why is toner used in laser printers instead of traditional ink?
Toner is used in laser printers due to its composition of pigment and plastic particles. The powder forms high-quality images and text on paper when fused by the printer's heated fuser unit. Unlike traditional ink, toner does not smudge and dries instantly upon printing, making it ideal for high-definition, professional outputs.
What role does the drum unit play in laser printing?
The drum unit or photosensitive drum is a core component in laser printing. It interacts with the laser to capture the image of the printed page. As it rotates, the drum forms an electrical charge pattern corresponding to the image, which attracts toner particles for transfer to the paper.
How do laser printers contribute to sustainability?
Laser printers contribute to sustainability in several ways. The toner used lasts longer than traditional ink, reducing waste. Additionally, modern laser printers feature energy-efficient designs with standby and deep-sleep modes that significantly lower power consumption, leading to less environmental impact.


